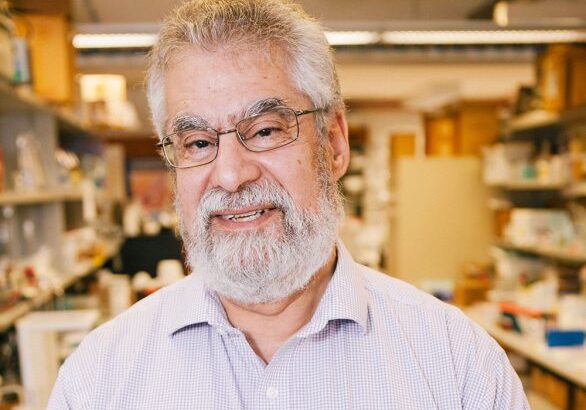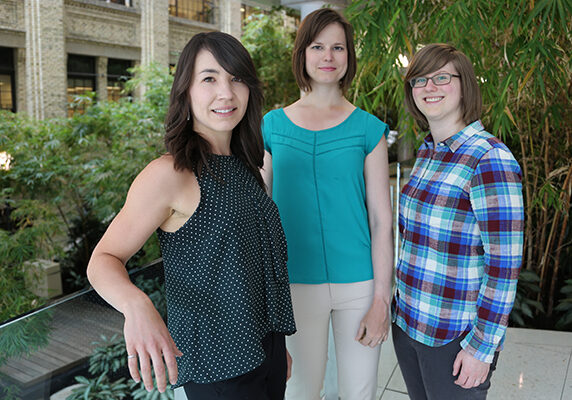
Simple attraction: U of T Engineering researchers control protein release from nanoparticles without encapsulation
Discovery stands to improve reliability and fabrication process for treatments for chronic conditions and serious injuries such as spinal cord damage and stroke
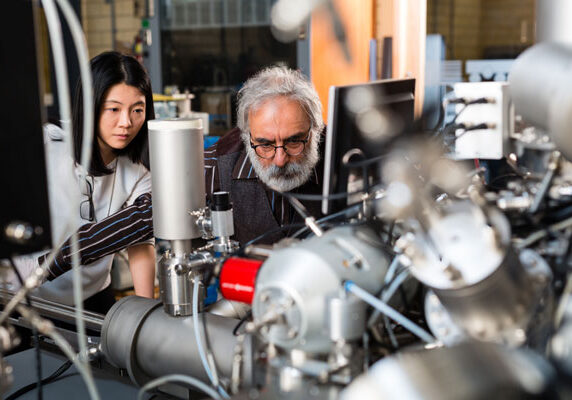

OCCAM: Advancing research from the depths of the ocean to outer space
The Ontario Centre for the Characterization of Advanced Materials (OCCAM) — a $20 million analytical laboratory at U of T Engineering — has officially unveiled its newest machines and is ready to take on new industrial partnerships
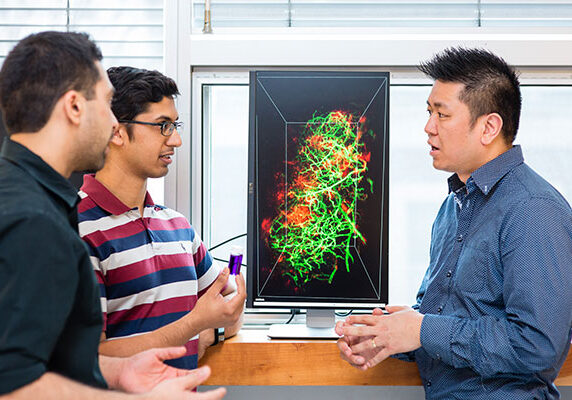

Tracking nanoparticles with transparent organs to help fight cancer and other diseases
An improved technique for clarifying organs can help researchers learn how nanoparticles might be used to diagnose or treat diseases like cancer
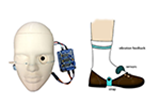
Two innovative biomedical devices from the Hammers & Nails Initiative
Collaboration with SickKids leverages engineering design to solve everyday challenges in hospitals

How many nanoparticle-based drugs reach tumours? Less than one per cent, U of T Engineering study shows
“Reality check” meta-analysis published in Nature Reviews Materials reveals that only 0.7 per cent of designer nanoparticles reach their intended target

Two CREATE grants boost U of T Engineering research into optical technology and lab-grown human tissues
Two CREATE grants received by Professors Peter Herman and Milica Radisic will help train a new generation of experts in optical technologies and tissue engineering

An engineering road map for scaling up production of stem cell-derived treatments
Yonatan Lipsitz and his co-authors have created a road map for the emerging industry of manufacturing stem cell therapeutics



